Curve Point Distribution
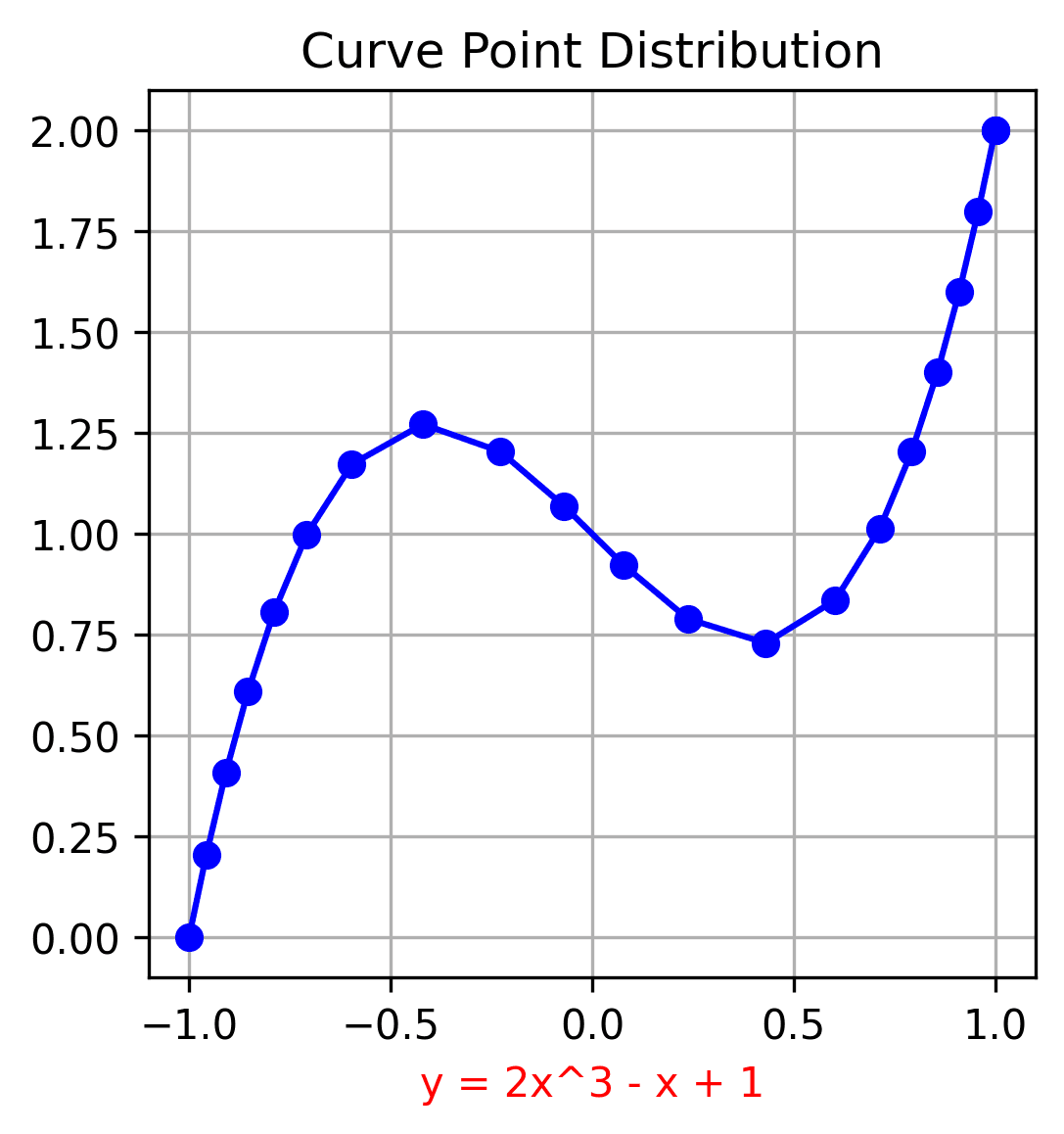
This implementation’s purpose is to distribute a desired number of points on the curve by equal path distance to each other. To do that, I applied an adaptable unit length strategy while trying to keep the segment length error percent is less than 1% by sweeping small increments on x axis . Later on, I will work on some improvements to reduce errors.
Here, I chose the curve function y = 2x^3 – x + 1 within [-1, 1] range by 20 points and 0.001 delta_x:
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import quad
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Point:
def __init__(self, _x, _y):
self.x = _x
self.y = _y
def function(x):
# Taking quadratic function y = 2x^3 - x + 1 as an example
return 2 * x**3 - x + 1
def integrand(x):
return np.sqrt(36 * x**4 - 12 * x**2 + 2)
def curve_Length(a, b):
curveLength, _ = quad(integrand, a, b)
return curveLength
def calculate_Curve_Points(numPoints, deltaX, a, b):
curvePointCoordinates = []
# First point as a reference start (lower bound)
x = a
y = function(x)
curvePointCoordinates.append(Point(x, y))
# Sweeping from lower bound to upper bound to get x axis value
# First and last point calculations are excluded
for k in range(numPoints - 1):
delta_x = deltaX
lowerBound = curvePointCoordinates[k].x
# Adaptable unit length after each error margin
unitLength = curve_Length(lowerBound, b) / (numPoints - 1 - k)
while True:
upperBound = lowerBound + delta_x
segmentLength = curve_Length(lowerBound, upperBound)
# Error percentage
error = 100 * abs(unitLength - segmentLength) / unitLength
if error <= 0.1 or segmentLength >= unitLength:
x = upperBound
y = function(x)
curvePointCoordinates.append(Point(x, y))
print("The error of segment", k+1,":", round(error, 2), "%")
break
delta_x += deltaX
# Last point
x = b
y = function(x)
curvePointCoordinates.append(Point(x, y))
# Extract x and y coordinates from curve_point_coordinates
x_coords = [point.x for point in curvePointCoordinates]
y_coords = [point.y for point in curvePointCoordinates]
# Plot the curve
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.plot(x_coords, y_coords, marker='o', linestyle='-', color='b')
plt.title('Curve Point Distribution')
plt.xlabel('y = 2x^3 - x + 1', color='r')
plt.grid(True)
plt.gca().set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box') # Set equal aspect ratio
plt.show()
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
numPoints = 20
deltaX = 0.001
a = -1.0 # lower bound
b = 1.0 # upper bound
calculate_Curve_Points(numPoints, deltaX, a, b)
[1] Arc Length Formula [2] Desmos calculator