Hamming, Blackman, and Blackman-Harris
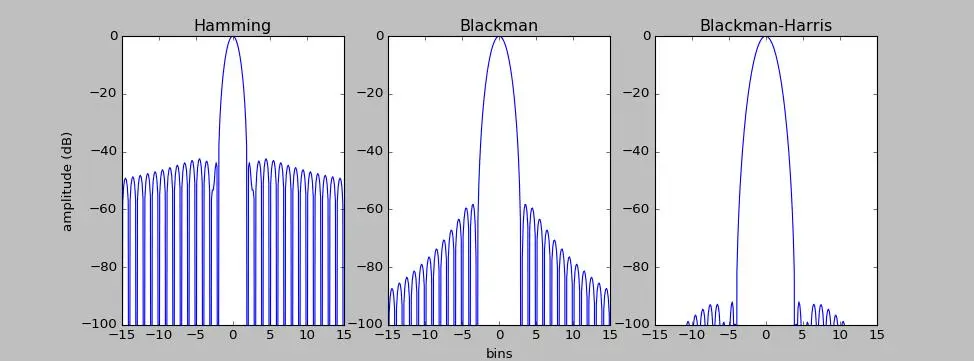
This is my implementation for some of windows used in audio applications. I chose Hamming, Blackman, and Blackman-Harris window functions. Instead of using FFT pack, I directly applied DFT since the DFT size is not too big. I scaled the amplitude for a better view. In the figure, we see their main-lobe width and side-lobes. The main lobe and the highest side lobe are important for us. I chose the small window and DFT sizes (64 and 512).
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def WindowFreqResponses(M = 64, N = 512):
#Window and DFT sizes have to be even
#HAMMING WINDOW
nh = np.arange(-M/2, M/2)
w1 = 0.54 + 0.46 * np.cos(2 * np.pi * nh / M)
#BLACKMAN WINDOW
nb = np.arange(0, M)
w2 = 0.42 - 0.5 *np.cos(2 * np.pi * nb / M) + 0.08 * np.cos(4 * np.pi * nb / M)
#BLACKMAN-HARRIS
nbh = np.arange(-M/2, M/2)
w3 = np.zeros(M)
coefficient = [0.35875, 0.48829, 0.14128, 0.01168]
for i in range(0, 4):
w3 += coefficient[i] * np.cos(2 * np.pi * i * nbh / M)
w3 = w3 / M
#Taking DFT and plotting for each window
plt.subplot(131)
DFT(w1, M, N)
plt.title('Hamming')
plt.ylabel('amplitude (dB)')
plt.subplot(132)
DFT(w2, M, N)
plt.title('Blackman')
plt.xlabel('bins')
plt.subplot(133)
DFT(w3, M, N)
plt.title('Blackman-Harris')
plt.show()
return
def DFT(w, M, N):
hWindow = int(M/2) #Half of window size
fftbuffer = np.zeros(N) #Zero-padding
fftbuffer[:hWindow] = w[hWindow:]
fftbuffer[N-hWindow:] = w[:hWindow]
#DFT Calculation
X = np.array([])
for k in range(N):
s = np.exp(-1j * 2 * np.pi * k * np.arange(N)/ N)
X = np.append(X, sum(fftbuffer*s))
mX = abs(X) #Amplitude
mX[mX < np.finfo(float).eps] = np.finfo(float).eps #For machine epsilon
mXdb = 20*np.log10(mX) #Amplitude in dB
hDFT = int(N/2) #Half of DFT size
scaledmX = np.zeros(N) #For a better view
scaledmX[:hDFT] = mXdb[hDFT:]
scaledmX[hDFT:] = mXdb[:hDFT]
plt.plot(np.arange(-N/2,N/2)/float(N)*M, scaledmX - max(scaledmX), 'b')
plt.axis([-15, 15, -100, 0])
return
###
WindowFreqResponses()The results are (approximately):
Hamming: Main lobe width is 4 bins and side-lobe level is -42.7 dB.
Blackman: Main lobe width is 6 bins and side-lobe level is -58.2 dB.
Blackman-Harris: Main lobe width is 8 bins and side-lobe level is -92 dB.
References:
[1] Mathematics of the Discrete Fourier Transform, Julius O. Smith III [2] FFT Bin Interpolation, Ted Knowlton [3] Windows, Matlab Documentation